Google DeepMind introduced the FACTS Grounding system in December 2024, which could revolutionise the evaluation of large language models' (LLMs) factuality. This benchmark is the first to enable automated verification of responses based on long documents of up to 32,000 tokens, with a particular focus on source fidelity and factuality.
The system's uniqueness lies in its two-level evaluation process and comprehensive test suite. The 860 public and 859 private test cases cover five key areas: medical (29%), legal (22.2%), internet/technology (19.2%), financial (18.1%), and retail (11.4%) topics. In the first evaluation phase, the system filters out responses that do not meet user requests; then, in the second phase, it analyses the factuality of the remaining responses relative to the source text. For reliability, the combined decision of three leading large language models - Gemini 1.5 Pro, GPT-4o, and Claude 3.5 Sonnet - is used, as researchers have shown that models typically evaluate their outputs 3.23% more favourably compared to those of other models.
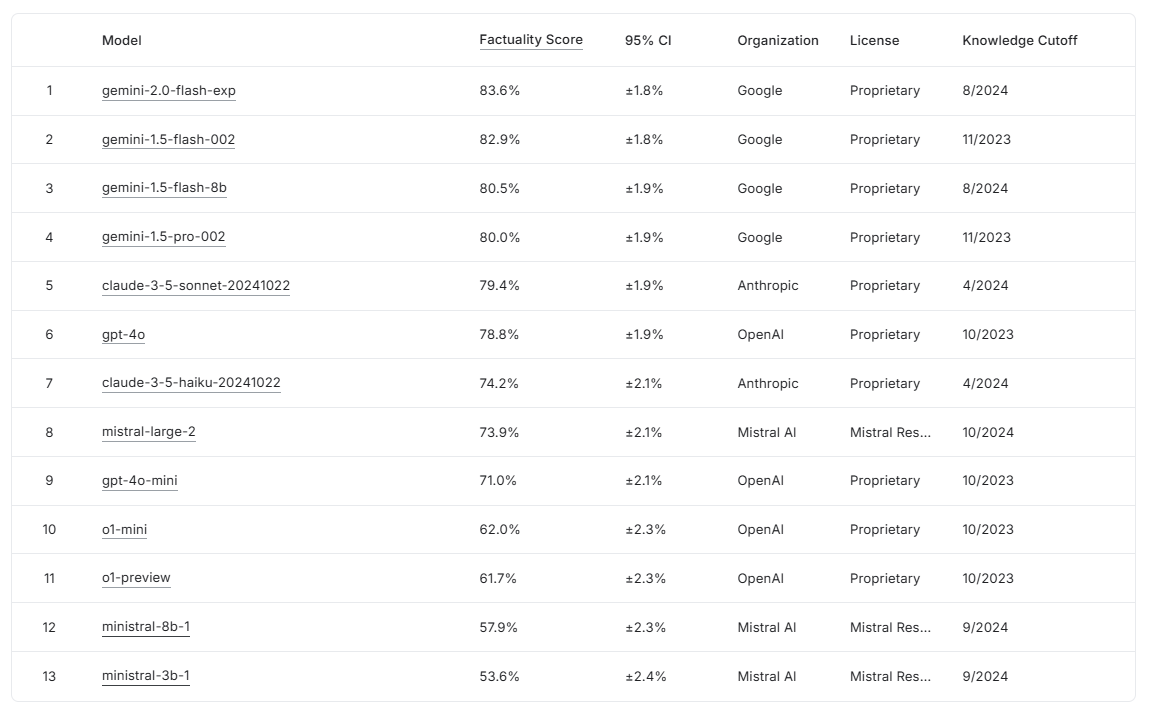
The initial tests yielded exciting results: Gemini 2.0 Flash Experimental achieved the best performance with a score of 83.6%, closely followed by Gemini 1.5 Flash (82.9%) and Gemini 1.5 Pro (80.0%). Notably, after filtering out inappropriate responses, a 1-5% decrease was observed in the final scores, indicating the stringent evaluation criteria. The benchmark is freely accessible on the Kaggle platform (www.kaggle.com/facts-leaderboard), allowing any researcher or developer to test their model. The system could be beneficial when accuracy and source fidelity of generated texts are critical, such as in the automated processing of medical documentation or legal texts.
Sources:


DeepMind's research paper on evaluating factual consistency in AI-generated text.