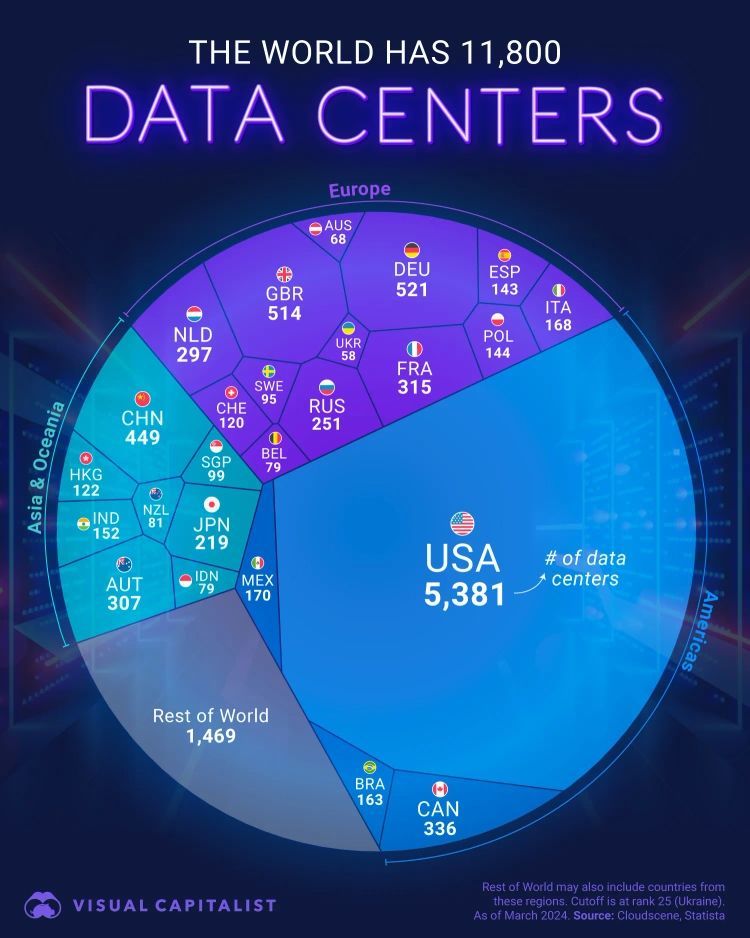
Data centers form the backbone of the digital ecosystem, and their geographical distribution provides a significant strategic advantage to the United States. The United States hosts 45.6% of the world's 11,800 data centers, far exceeding countries such as Germany and the United Kingdom (4.4% each) or China (3.8%). This concentration enables the US to exert substantial influence over cyberspace governance, directly affecting global digital policies.
The Stargate alliance announced in January 2025 between OpenAI, Oracle, and Softbank may further strengthen this dominance, as the project, backed by the Trump administration, plans to invest $500 billion in artificial intelligence infrastructure over the next four years, expanding its network of data centers and reinforcing US technological leadership. The operation and evolution of data centers is moving towards cloud-based technologies, where virtual data centers can be provisioned or scaled down with just a few clicks, providing significant advantages for companies moving to the cloud. In modern data centers, software-defined networking (SDN) manages traffic flows, whilst Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) offerings hosted on private and public clouds spin up systems on-demand. Global data traffic is expected to reach 181 zettabytes by 2025, representing an almost 90-fold increase compared to data consumption in 2010, further underscoring the need for scalable infrastructure to meet growing data processing and storage demands.
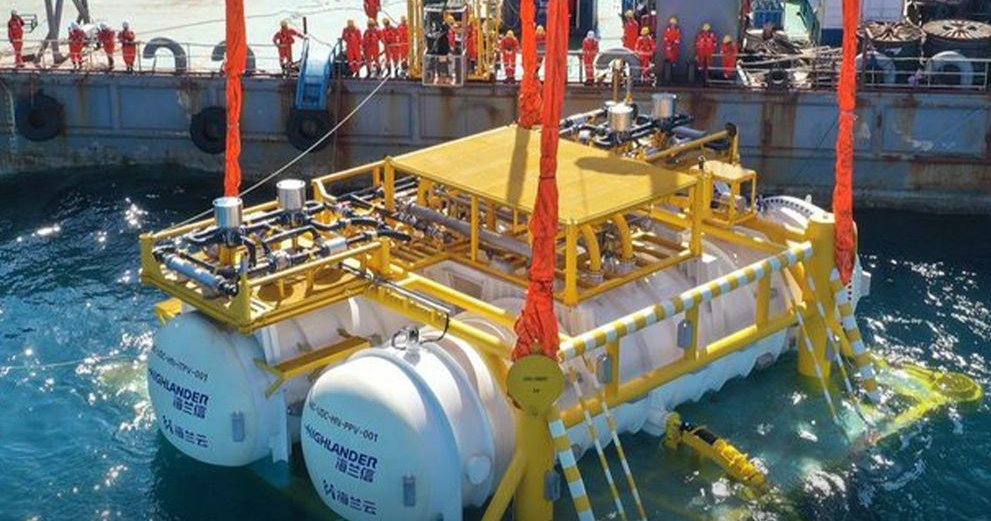
However, the rapid expansion of data centers also presents significant environmental challenges, as these facilities require increasing amounts of energy and water for their operation and cooling, and are responsible for generating a growing residual footprint. China's expansion of its underwater data center, which added a new module containing 400 high-performance servers in February 2025, demonstrates the search for alternative cooling solutions, as this facility uses seawater as a natural coolant. Countries without significant data center infrastructure depend on the United States for data access and storage, resulting in geopolitical submission already in place, whilst various data center security solutions, such as Check Point Maestro hyperscale security, become vital in defending against cyber threats.
Sources: